Importance of FLU Vaccines for the Elderly
According to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, each year, around 5% to 20% residents in the US get a flu shot. More than half of these 200,000 Americans are 65 years old or above and get hospitalized due to the flu. Moreover, 90% of the deaths that occur in these people are due to complications brought on by the flu.
Why Does This Happen?
As people get older, they stop taking vaccines, which weakens their immune system and leaves them vulnerable to all kinds of diseases. In older people, the immunity from certain diseases wears off as time passes. In adults, these illnesses cause a minor setback but in older adults, it can become life-threatening.
A simple cough or cold might be something that an adult experience when they are passing by an unhygienic site but for older adults, those suffering from chronic disease, their condition can worsen.
The problem with symptoms of flu is that they appear suddenly. Older adults must seek medical attention immediately and get antiviral medicine, which helps reduce the symptoms within two days.
Here are a few symptoms of influenza:
- Cough (usually dry)
- Fatigue
- Sore throat
- Chills
- Sudden high fever
- Runny nose
- Nasal congestion
- Joint pain, muscle aches and headache
- Other symptoms include diarrhea, vomiting or nausea (rare)
Flu Risk Factors
Having the following diseases place older adults at a higher risk of becoming seriously ill due to the flu:
- Chronic kidney disease
- Heart disease
- Morbid obesity
- Chronic lung diseases like bronchiectasis, asthma, COPD, or cystic fibrosis
- Liver disorders
- Severe anemia
- Chronic metabolic disorder
- Diseases (HIV, AIDS)
- ong-term exposure to aspirin therapy, chemotherapy or steroids
Protection against Influenza
The antigen present in the vaccine triggers the body to produce antibodies, which helps protect the immune system and wards off any contagious influenza symptoms.
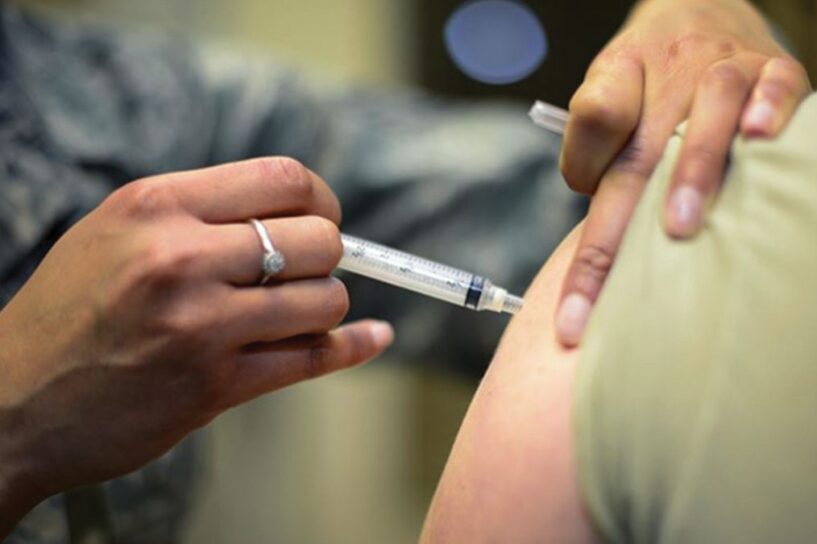
CDC recommends that all older adults must get a vaccination every year. According to CDC, the “flu season”, when most of the flu activity happens, occurs in the months of October and November.
For seniors, there are 2 flu vaccine options: for people aged 65 or older, they can either get the regular dose or the high-dose. The high-dose has 4 times more the antigen, which is more effective. According to the New England Journal of Medicine, the efficacy of the higher dose was tested, which showed results that this dose is 24% more effective for older adults.
Since it contains more antigen, older adults might experience a few side effects such as swelling, pain and redness at the site of injection including muscle ache, headache and general discomfort.
For older adults, those suffering from any kind of lung diseases like asthma or chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD), the risks are a double whammy. They have to be in tune with their body to notice the slightest of changes. Something as small a cough can cause serious complications and land them in a hospital for days.